
This metric is especially useful when comparing companies or evaluating a company’s financial health over time. By excluding exceptional items, normalized net income reveals the underlying financial performance and shows how well the company is performing in its core business operations. Normalized net income plays a crucial role in evaluating a company’s financial health, as it provides net income recognition always increases: a clearer picture of its ongoing operational performance. The metric provides a cleaner, more reliable figure that can guide investment decisions, strategic planning, and overall financial analysis.
- It removes the noise from non-recurring events, allowing stakeholders to focus on what truly matters — the company’s ability to generate sustainable profits.
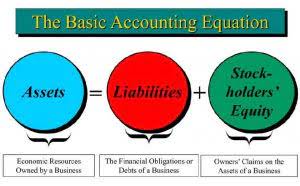
- Normalized net income refers to a company’s earnings after adjusting for one-time events, such as gains, losses, or irregular income.
- Yes, if a company’s core operations are not profitable, even after excluding one-time events, it can report negative normalized net income.
- Normalized net income excludes non-recurring events like one-time gains, losses, or extraordinary items, while regular net income includes everything.
- The normalized net income of $5,700,000 reflects a more accurate picture of the company’s ongoing operations and its capacity to generate profit from its core business activities.
Excludes Important Items
Yes, if a company’s core operations are not profitable, even after excluding one-time events, it can report negative normalized net income. Analysts prefer normalized net income because it offers a clearer picture of a company’s true profitability and is useful for comparing companies and assessing long-term performance. Normalized net income refers to a company’s earnings after adjusting for one-time events, such as gains, losses, or irregular income. These adjustments provide a clearer picture of a company’s ongoing profitability, removing any distortions that could result from non-recurring items. Positive normalized net income signals strong operational health and contra asset account can lead to stock price appreciation. Normalized net income excludes non-recurring events like one-time gains, losses, or extraordinary items, while regular net income includes everything.

How does normalized net income affect stock price?
Some significant but non-recurring items, like legal settlements or environmental costs, may not be included in the normalization process, Partnership Accounting potentially overlooking major risks. Different analysts may adjust for different items, which can lead to inconsistencies.
How to Find Normalized Net Income?
It removes the noise from non-recurring events, allowing stakeholders to focus on what truly matters — the company’s ability to generate sustainable profits. It’s important to consider other financial metrics, such as cash flow, balance sheet strength, and debt levels, to get a complete picture. In this case, the company’s net income was adjusted for the one-time gain from the sale of property and for restructuring charges and impairment losses. Without these adjustments, the reported net income of $5,000,000 could give investors the impression that the company is performing worse or better than it truly is. The normalized net income of $5,700,000 reflects a more accurate picture of the company’s ongoing operations and its capacity to generate profit from its core business activities.

Commentaires récents